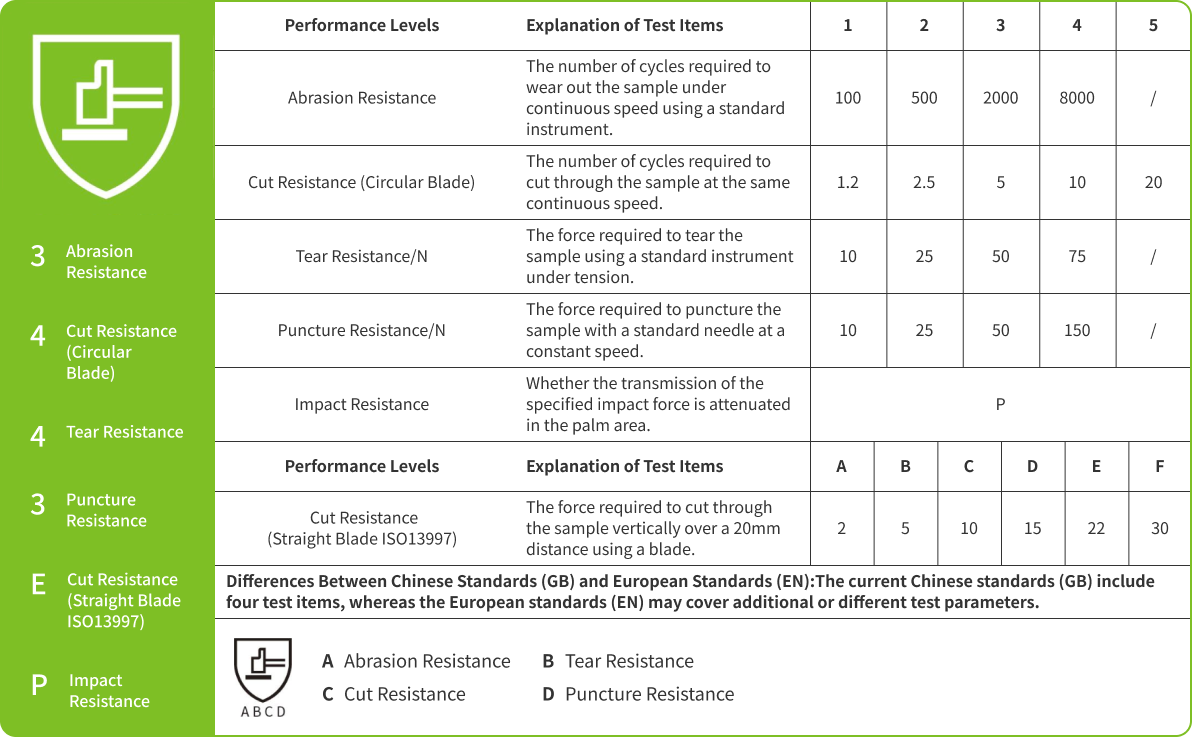
EN388 is a European standard for testing and certifying the mechanical performance of protective gloves, evaluating their ability to provide mechanical protection in industries such as manufacturing, construction, and metalworking. This standard applies to work environments requiring protection against risks such as cuts, abrasion, tearing, and puncture.
EN374-1:2016:This standard addresses protection against microorganisms and chemical hazards. It specifies the ability of glove materials to resist permeation by potentially hazardous non-gaseous chemicals under continuous contact conditions. It defines the chemicals and levels required for testing.
EN374-2:2014:Penetration resistance testing is used to determine the porosity, holes, and micro-defects of protective gloves, ensuring that chemical molecules and/or microorganisms do not diffuse. It includes water and air penetration tests.
EN374-4:2013:Determination of resistance to degradation by chemicals. This involves testing the degradation resistance of glove materials caused by chemicals and the permeation of chemical molecules through glove materials. It replaces the former EN374-3.
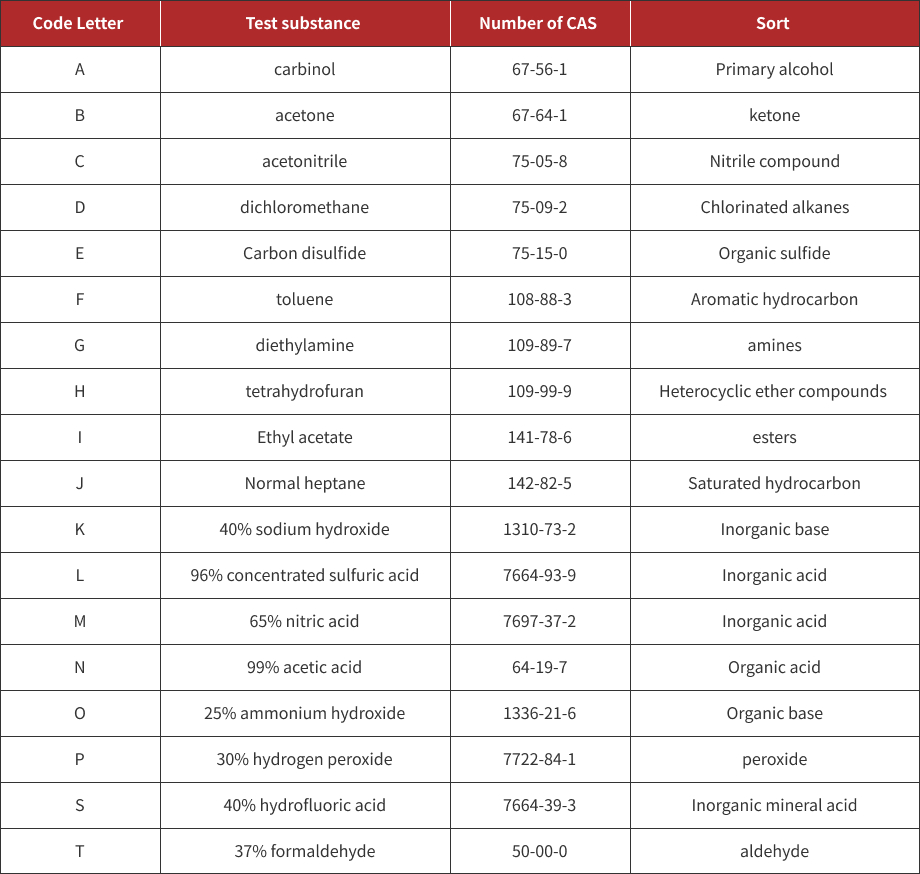
List of chemicals used for testing(gb28881)
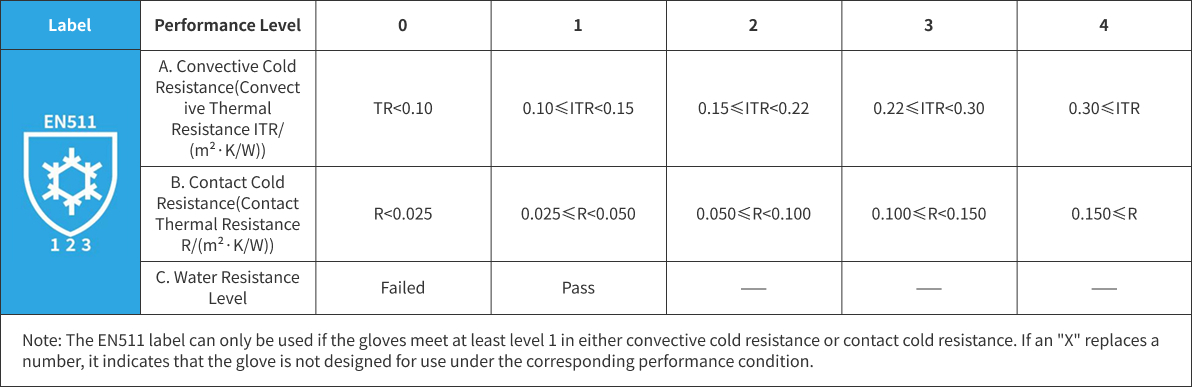
EN 511 is a European standard specifying the performance requirements and test methods for gloves designed to protect against cold. The standard defines requirements for thermal insulation and water resistance, ensuring effective protection in cold and wet environments.
Suitable for gloves used in climates or activities with temperatures as low as -50°C to prevent cold-related injuries.
Cold protection gloves must have abrasion resistance and tear resistance of at least level 1. Coated cold protection gloves must also demonstrate resistance to flex cracking.
Cold protection gloves must undergo water resistance testing. If rated as level 0, a warning must be provided indicating that the gloves may lose their cold protection properties when wet.
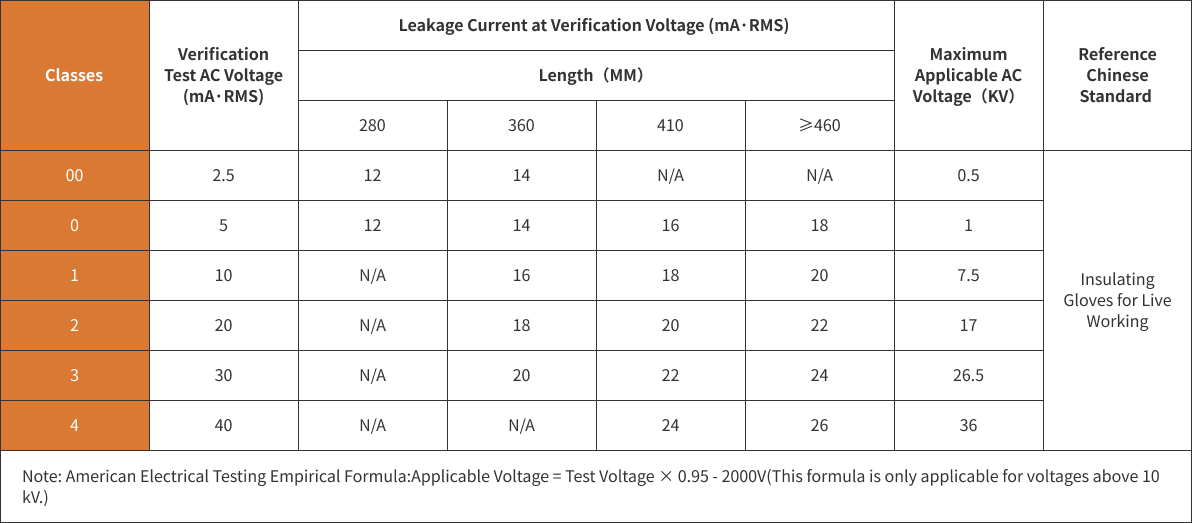
EN60903:2003 is a European standard that specifies the safety requirements and testing methods for electrical insulating gloves. This standard applies to insulating gloves used in the electrical power industry, ensuring effective protection in high-voltage environments. The standard covers material performance, design requirements, labeling, and testing methods, including the evaluation of insulation properties, puncture resistance, and chemical resistance.
Gloves that comply with the EN60903:2003 standard effectively reduce the risk of electrical accidents, enhance operational safety, and ensure the personal safety of electricians working in high-voltage conditions.
EN407:2020 specifies the requirements for gloves and other hand protection equipment designed to protect against thermal hazards (heat and/or fire). Compared to the 2004 version, the performance levels remain unchanged, but the labeling has been updated. The new standard evaluates performance based on the minimum test value rather than the average.
Key Updates in EN407:2020:
Tear Resistance: Products must achieve at least level 1 tear resistance (tested according to ISO 23338).
Glove Length for Metal Splash Protection: Gloves designed to protect against metal splashes (including small and large splashes) must meet the following minimum length requirements:
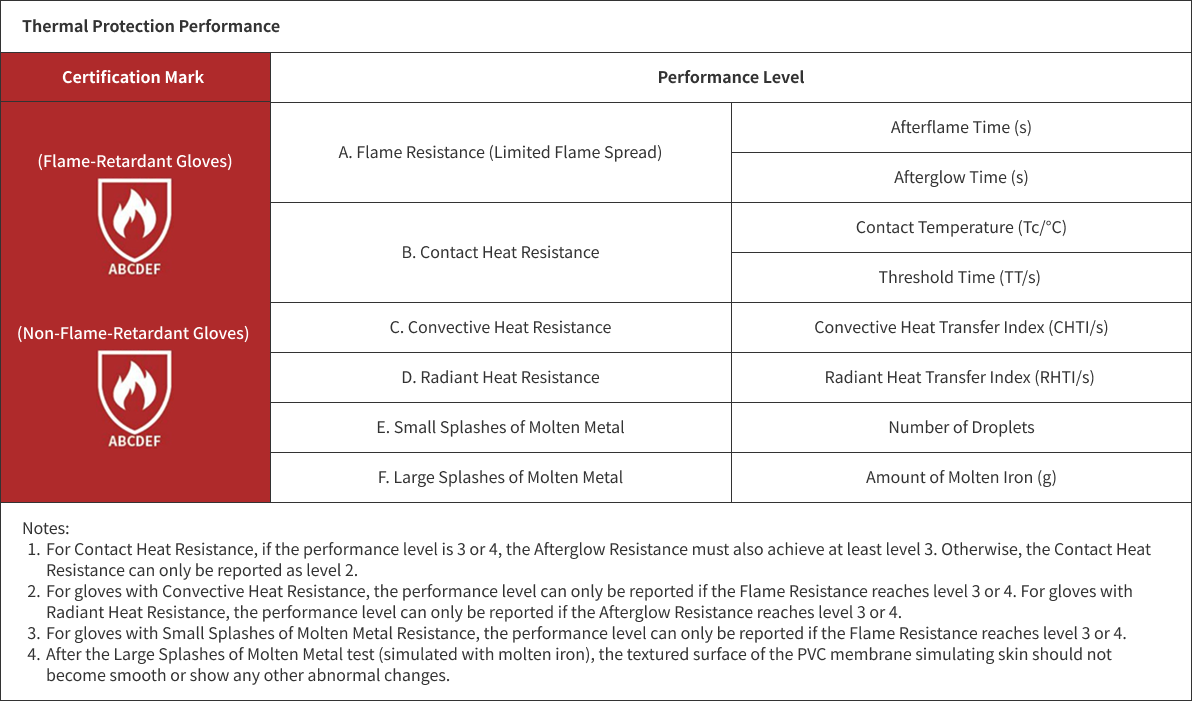
GB/T38306 - Hand Protection Gloves Against Thermal Hazards
This standard applies to gloves designed to protect against one or more forms of thermal hazards, such as flames, contact heat, convective heat, radiant heat, small splashes of molten metal, or large splashes of molten metal. It does not apply to gloves used for firefighting or welding operations.
Abrasion Resistance and Tear Resistance: Gloves must achieve at least level 1 in both abrasion resistance and tear resistance.
This standard applies to gloves designed to protect the wearer's hands from ionizing radiation and radioactive contaminants in work areas, gloves installed in permanent sealed chambers, and intermediate sleeves between gloves and permanent sealed chambers.
Exclusions: This standard does not apply to medical radiation protection gloves.
Radiation Absorption Efficiency: The radiation absorption efficiency of glove materials is expressed in terms of lead equivalent thickness. The protective material of the gloves must have a lead equivalent thickness of at least 0.05 mm.
Airtightness Test: Gloves must pass an airtightness test.
Mechanical Hazard Protection: At least one mechanical hazard protection performance must meet or exceed level 1 as specified in GB24541. Otherwise, the glove's user instructions must clearly state: "This glove does not provide mechanical hazard protection."
EN455:Performance requirements and testing for disposable medical examination gloves. This is a German and European standard for medical examination gloves, specifying product integrity, physical performance, and biological protection requirements and testing.
ASTMD6319:Performance requirements and testing for disposable nitrile rubber medical examination gloves. This is an American standard for medical examination gloves.
GB15979:Specifies the hygiene standards for disposable sanitary products, including production environment hygiene standards, disinfection effectiveness bio-monitoring evaluation standards, and corresponding testing protocols.
GB10213:Specifies the requirements for sterilized or non-sterilized rubber examination gloves used to prevent cross-infection between patients and users during medical examinations and diagnostic procedures. It also includes rubber examination gloves for handling contaminated medical materials.
Industrial Disposable Gloves: Must comply with EN420 and ISO/EN374-5, ensuring ergonomic design and passing airtightness and watertightness tests. For gloves with minor chemical resistance, EN374-1:2016 testing is required.